OLED is an organic LED. This post explains what it is, how it works, what serves, and a comparison with other technologies.
To know how the LED works, click in this button.
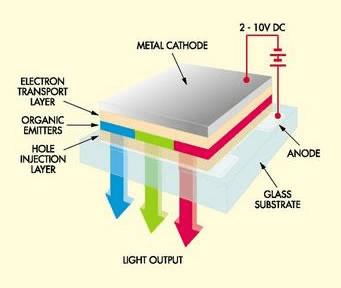
Structure and operation
Instead of doped silicon, OLED has an emissive layer and other conductive made of polymers based in carbon, have a total thickness between 100 and 150 nanometers. The cathode terminals, made of aluminum or calcium, stay on the side of emissive layer with electrons excess. While the anode terminals, usually made of indium tin oxide, stay between the substrate and conductive layer with a lack of electrons. The substrate is made of glass or plastic.

How the OLED emits light? When a voltage is applied in the terminals, electrons from cathode go to the emissive layer. While the holes (empty space without electrons) go to the conductive layer. When an electron fills a hole in the light-emitting layer (EML), between the emissive (ETL) and a conductive layer (HTL), the former loses energy and emits a photon, a light particle.

In practice, the OLED screen has many organic layers to increase efficiency and glass or plastic protection in the cathode.
Generating colors
An OLED pixel has three materials in the light emitter layer, each material is doped with an organic molecule so that the emitted light has a determined wavelength, which defines the color. The three materials are doped to emit in red, green, and blue colors.
This file in pdf shows all the materials used to manufacture OLED layers, click here to see.
Advantages over other technologies
- The OLED is more efficient and spends less energy than actual technologies;
- In opposite to LCD and LED TVs, the OLED type does not need a backlight. Allowing the construction of lighter and thinner monitors. Screens with this new technology have a wider angle vision;

- The OLEDs are easier to make than LEDs because the material isn’t crystalline, by that, don’t have a pattern molecular structure.
Applications
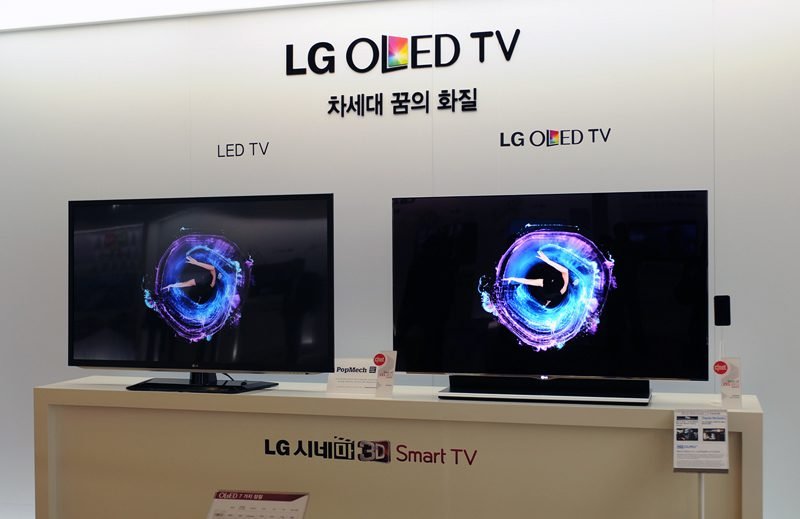
- OLED TVs have image quality much better than other television types that exist. However, have a smaller lifespan due to organic material;

- Small OLED screens will be used in cellphones, cameras, electronic games, etc. It already exists small OLED displays to make projects;


- This technology will allow the creation of flexible screen, which can be rolled up;
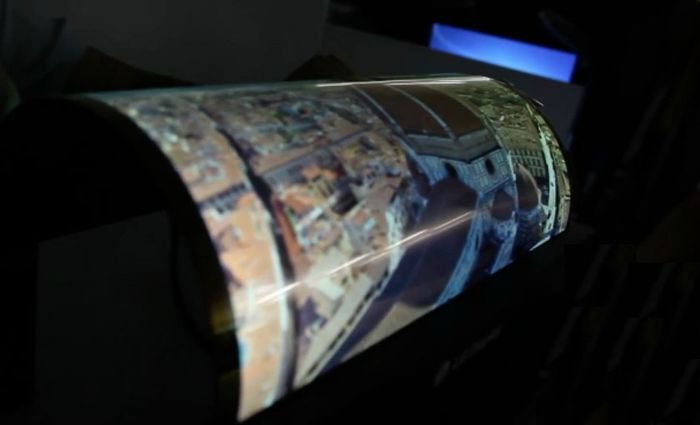

- The flexible screen can be use in wearable computers.





