Semiconductor or diode lasers are the most used nowadays. The operation and materials used in this type of laser are shown in this post.
Click on the following links to know laser’s operation and the first part respectively.
How do diode lasers work?
This type of laser was invented in 1962. In a semiconductor laser, the optical cavity is an intrinsic layer, by that, wasn’t doped to have lack or excess of electrons. It’s in between the semiconductors type P and type N. The thickness of layers are in nanometric scale.
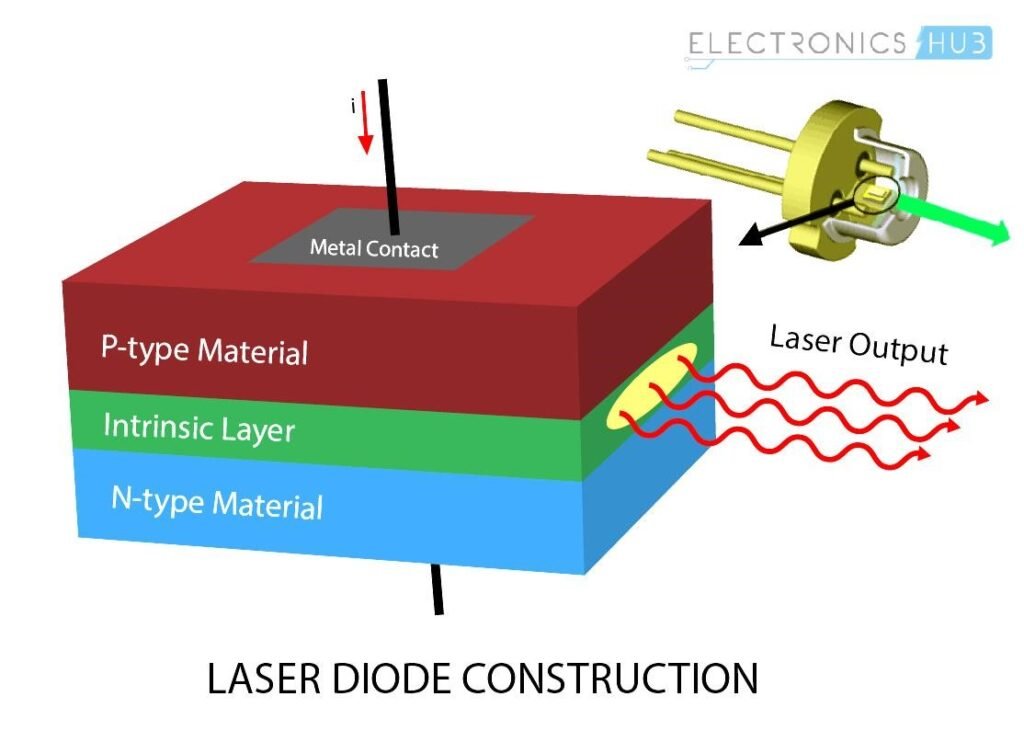
Electric current attracts electrons from N layer and the holes from type P to intrinsic layer. Holes are empty spaces without electrons, but are considered virtual particles with positive charge. When a free electrons combines with a hole, excess energy is emitted in form of a photon (light particle).
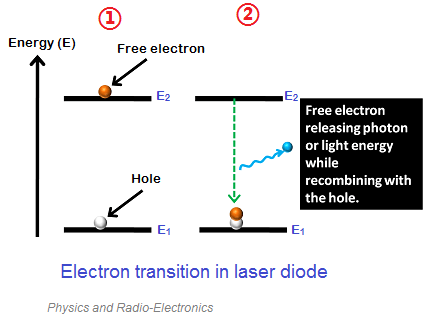
The produced photons by interactions between electrons and holes make the stimulated emission in other free electrons, emitting more photons. This phenomenon have already been explained in the post about laser operation. Some free electrons interact with valency electrons, putting the latter in a state of higher energy to then emit photons.


Semiconductor materials used
Laser’s wavelength depends on used material and semiconductors structure dimensions. The most used material as substrate for diode lasers is the galluim arsenide (GaAs). The applied elements to make the GaAs doping are silicon, aluminium and selenium. Wavelength is from 630 nm to 1050 nm, depending on materials used in doping.

Many semiconductor combinations are used for different applications. Another very applied materials as substrate are: indium phosphide (InP), gallium nitride (GaN) and gallium antimonide (GaSb).

Advantages and disadvantages of diode lasers
The advantages about other types of laser are:
- Intensity, polarization and phase are much easier to be controlled.
- Are cheaper than other types, allowing more production.
- Do not need mirrors.
- Can be smaller.
- Lower energy consumption.
While the disadvantages:
- Power is much lower than other types, limitating applications.
- Diode lasers are very sensible to temperature, it’s increase will reduce power output and increase beam’s divergence.



