Responding to requests, this post’s subject is industry 4.0. Also known as fourth industrial revolution, because it is a radical change in manufacturing.
What is industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is a concept which applies advanced technologies of information, control and automation to manufacturing process. It differs from other three industrial revolutions for placing more emphasis to optimization. The striking features of industry 4.0 are:
- Machines digitally connected to a computer network;
- Interconnectivity between machines and systems;
- Sensor networks to acquisition and treatment of data;
- Artificial intelligence conducting the productive process.
The creation of cyberphysical systems is the main difference from industry 4.0 to current 3.0. Are created with sensor networks, wireless communication between machines and systems, and software modelling. These new systems monitor the manufacturing process, create a virtual copy and take decisions.
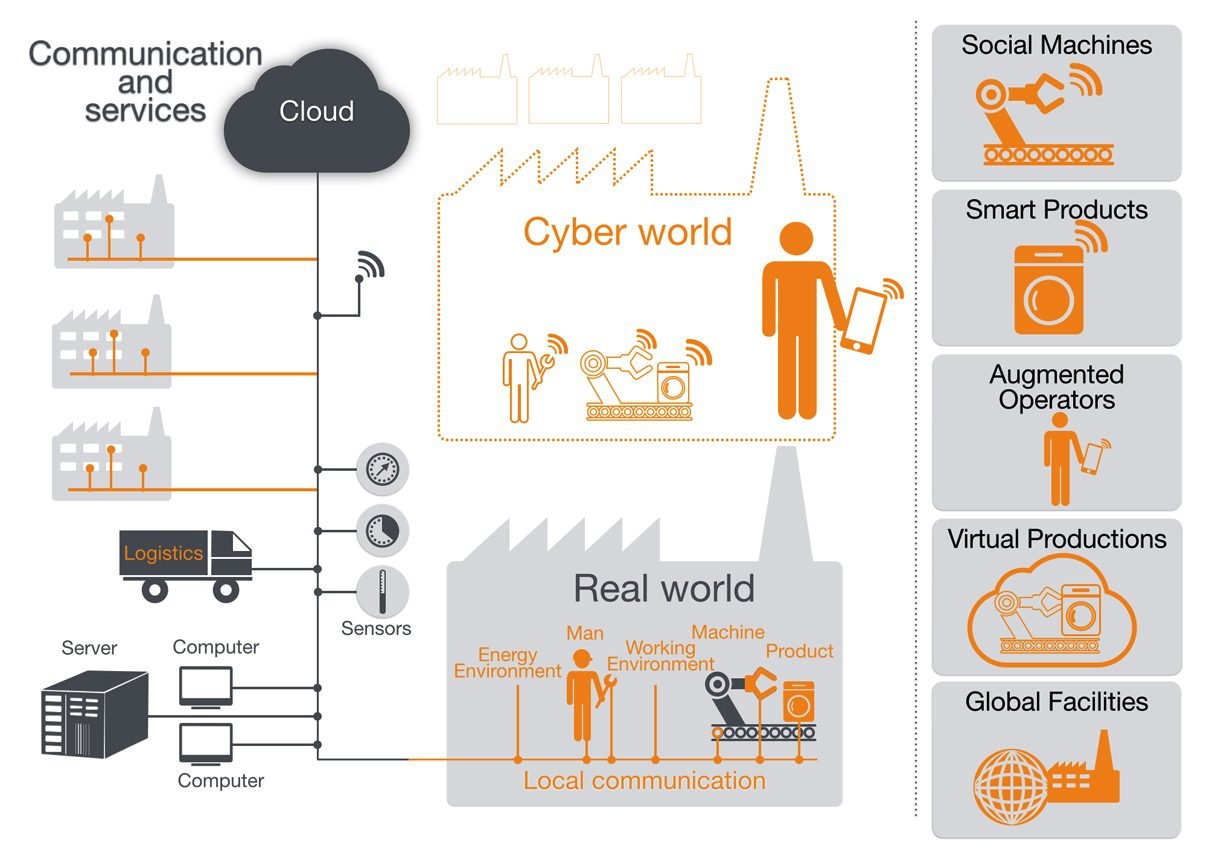
Industry 4.0 technologies
What are the technologies which characterize the fourth industrial revolution? I will write future posts about these technologies with more details, in this post is shown what are and how are used in smart factories.
Internet of Things (IoT)

Internet of Things is the idea to connect to internet objects which weren’t connected before. Are integrated to a computer network to communicate with other objects. In industry 4.0, robots, machine tools and other equipment will communicate and cooperate in real time.
Big Data
The machine and sensor networks produce big quantity of data. This collection of data is called Big Data. It has too much information and grow more in size and complexity. Therefore, needs special tools to deal with a growing Big Data, finding the necessary information to solve problems.
Cloud computing
Where to store this great quantity of data? Can be stored and processed in the internet, using online services which stay in a cloud. The cloud computing provides more speed, flexibility and economy. The clouds can be public, private or hybrid.

Cybersecurity
The Big Data information stored in cloud must be protected. A connected factory is subject to information theft, sabotage and even risk to workers. It is more vulnerable than an industry 3.0 factory.
Augmented reality
The augmented reality adds virtual objects to real world in real time. These objects can be seen through a tablet or smartphone’s camera and manipulated.

This technology can be applied in marking and identification of products. An augmented reality applicative reads the QR code of a product and shows information.

Additive manufacturing
With the invention of 3D printer, appear the concept of additive manufacturing, which is to create parts from digital 3D models and add material layers to have the desired form. It is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing, where a piece of material is machined (cut, pierced, etc), removing unnecessary parts until get the designed form.

Customized small pieces have a bigger cost benefit with additive manufacturing.



