Fulfilling requests, this post’s subject is the problem of electromagnetic interference (EMI). In addition to relation with electromagnetic compatibility.
What is it and how is electromagnetic interference generated?
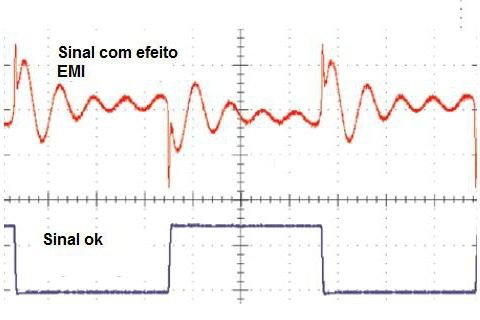
It is a phenomenon that causes undesirable effects and signals in electric and electronic equipment.
These signals can spread by conductive cables (can be from a power supply, signal, or grounding) magnetically coupled circuits, capacitive coupling, or electromagnetic waves, the latter can create an induced current in a conductor.

EMI signals vary from some kHz (kilohertz) to GHz (Gigahertz), whose amplitude and frequency can vary. Can be constant or short duration. Some sources of electromagnetic interference are:
- Spark generated in the combustion engine.
- GPS satellites.
- Cellphone towers.
- Brushes of electric motors.
- Radars.
- Electric circuits’ switching (constant change of state).
- Devices with Bluetooth.
- Power supply.
- Natural sources like atmospheric discharges, lighting, etc.
The effects can harm the equipment’s performance, simply prevent the operation, burn components, and in some cases, activate devices at the wrong time. For example, activate the car’s ABS brake when passes close to a radio station. Because of that, electronic devices must be off during flight’s take-off and landing.
Anechoic chamber
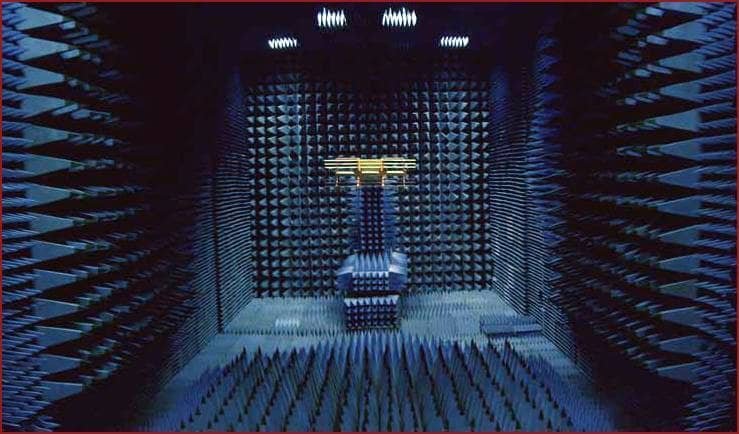

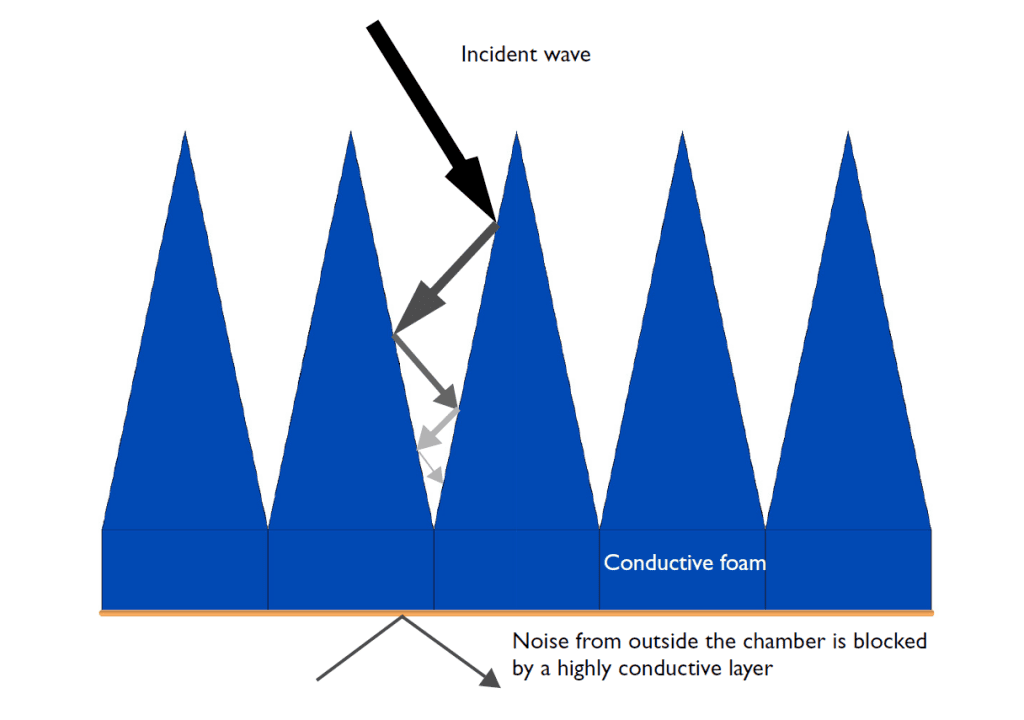
I was asked if is it possible to create a space without any electromagnetic energy. The answer is yes, this space is called anechoic chamber. Protects the interior for any external sound or electromagnetic wave. These rooms are used by universities and research centers to test audio equipment, antennas, radars, and other electric and electronic equipment without external interference.

In an anechoic chamber, it is possible to listen to your own breathing and heartbeat. Some chambers record negative levels of decibels, sound intensity measurement.
How does it work?
The sound is reflected in flat surfaces. Therefore, surfaces of internal walls are formed by wedges in the shape shown below, to dissipate waves.
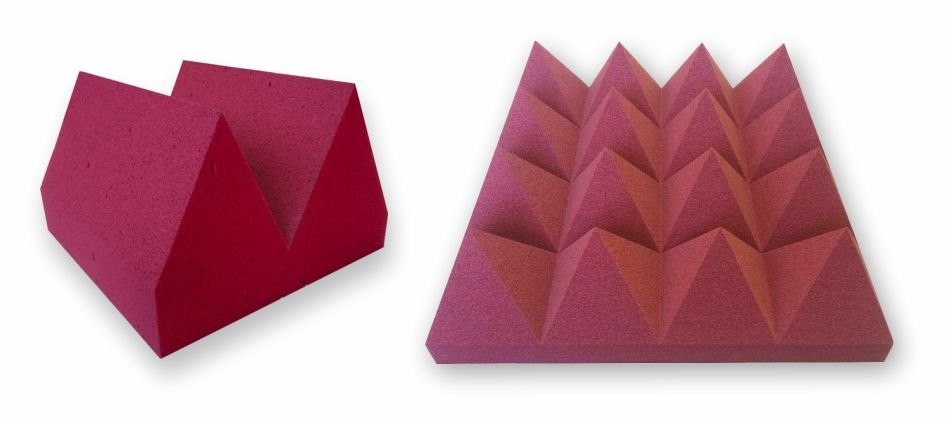

The material that is made of absorbs electromagnetic waves, usually is a conductive sponge.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is a concept, that attests to the capacity of a device or system to operate properly in an environment with electromagnetic waves from other sources. Exist national and international standards of EMC to reduce electromagnetic interference, which involves grounding, shielding of wires, etc. Currently, computational simulators are used to see electromagnetic fields, detect “accidental antennas” and correct EMI problems in the design phase.
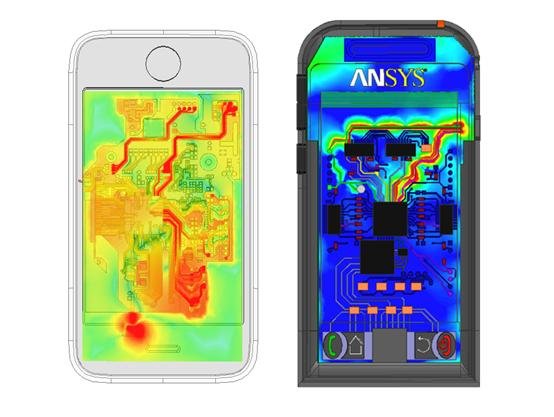

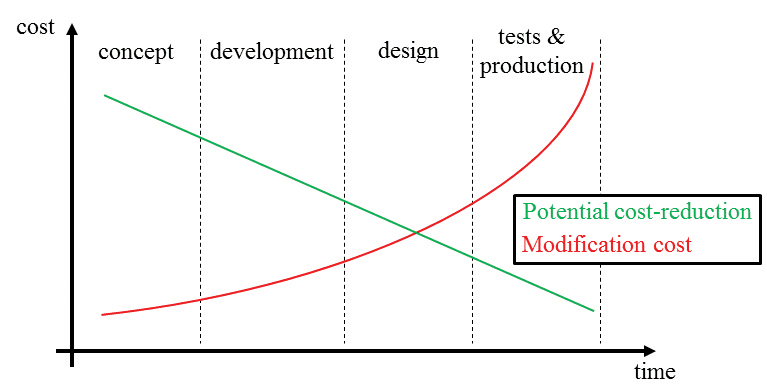
Some other measures to remove or reduce EMI are:
- Reduction of parasite capacitance and inductance in cables.
- Put filters in electronic circuits.
- Use tranced pair cables to cancel external interference and between wires.
- Avoid oxidation of components and boards.



