Continuing to Technical Museum Nikola Tesla series. Are shown another section and main hall. Other part are in following links.
Energy conversion Part 2

This area is close to entrance, in opposite side of another hall about energy conversion. This is a fuel tank rubberized inside. Used between 1941 and 1945.

A three-phase induction motor with slip rings, model NA 166/12, with 300 HP (220 kW) and 500 V. Manufactured by Magyar Siemens-Schuckert in Budapest, Hungary.

Starting device of three-phase induction motor, with water rheostat.

A direct current generator model GM-252, SZAM 6777, also from Magyar Siemens-Schuckert. Whose nominal values are: 38 kW, 110 V and 345 A.

Electronic microscope model EM-75 of Philips manufactured in 1963.

Marine telegraph with radio transmitter of Siemens.

4 poles direct current generator, model NP 22/25 from Siemens-Halske. Generated 220 V and 200 A.

12 poles DC generator, model ELIN GU-800. Voltage band between 120 V and 175 V, 840 kW power and 4800 A.

Protection switch for three-phase motor.
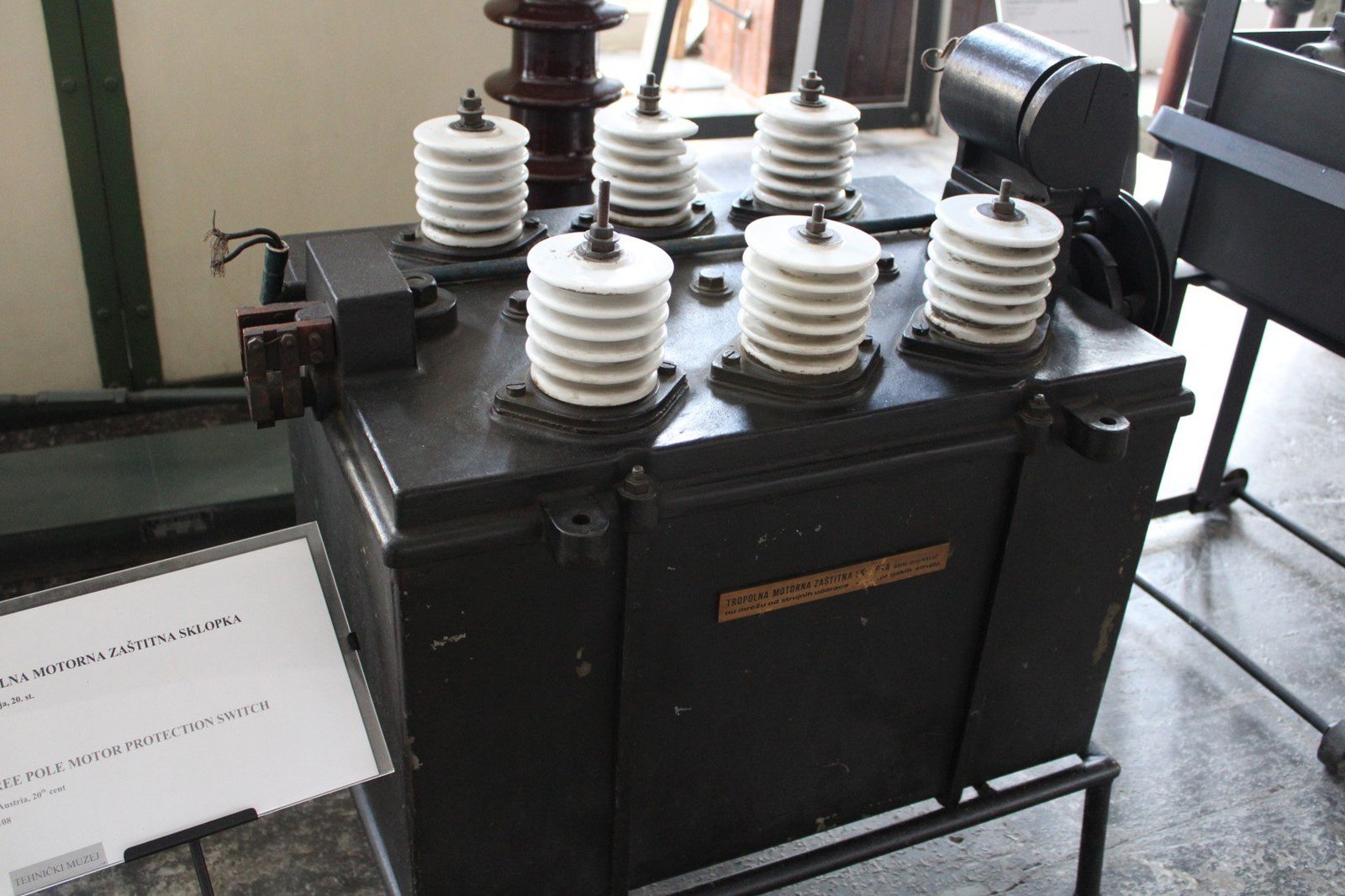
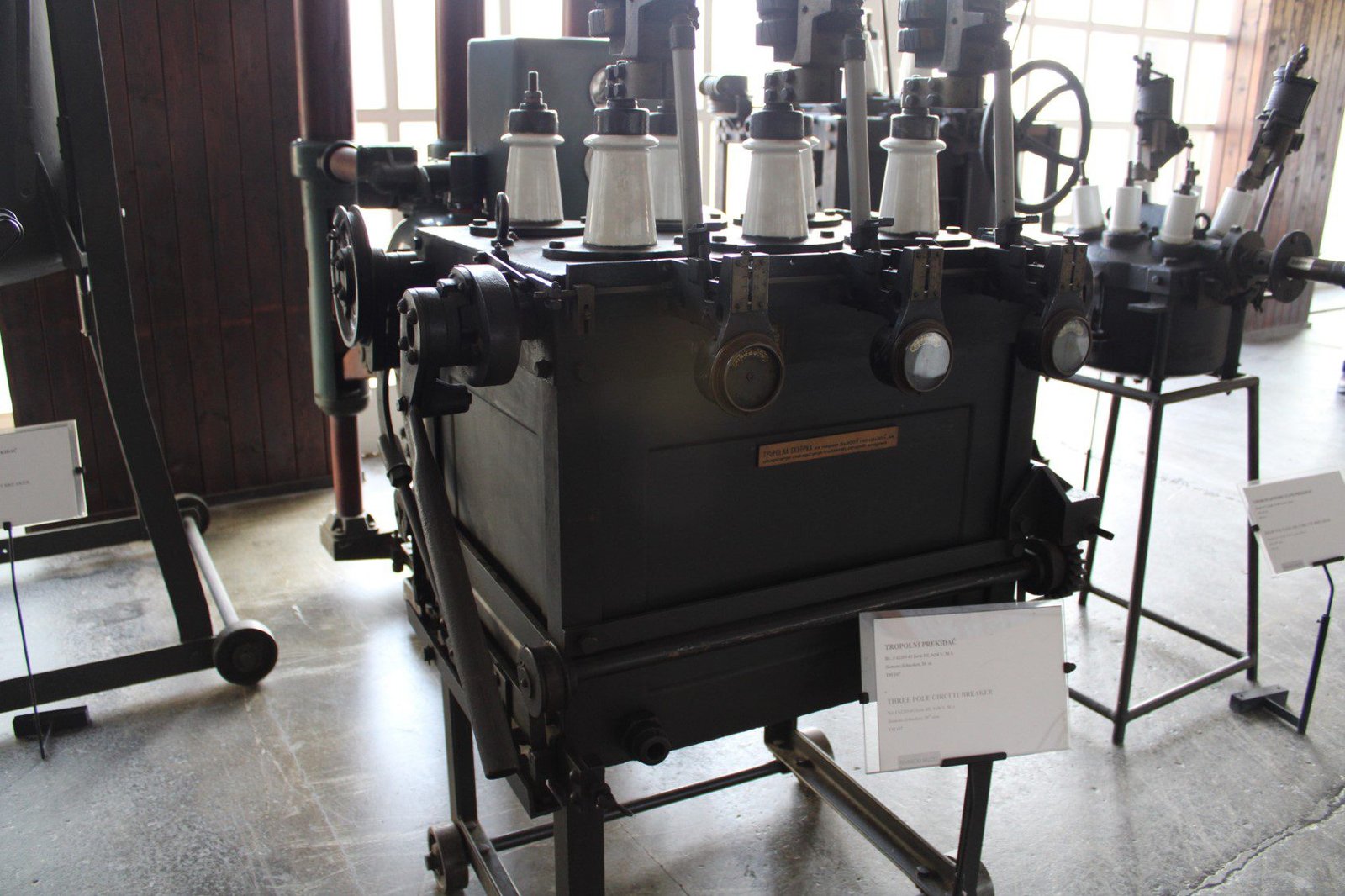
Three-phase circuit breaker of 3×50 V and 50 A. Made by Siemens-Schuckert.

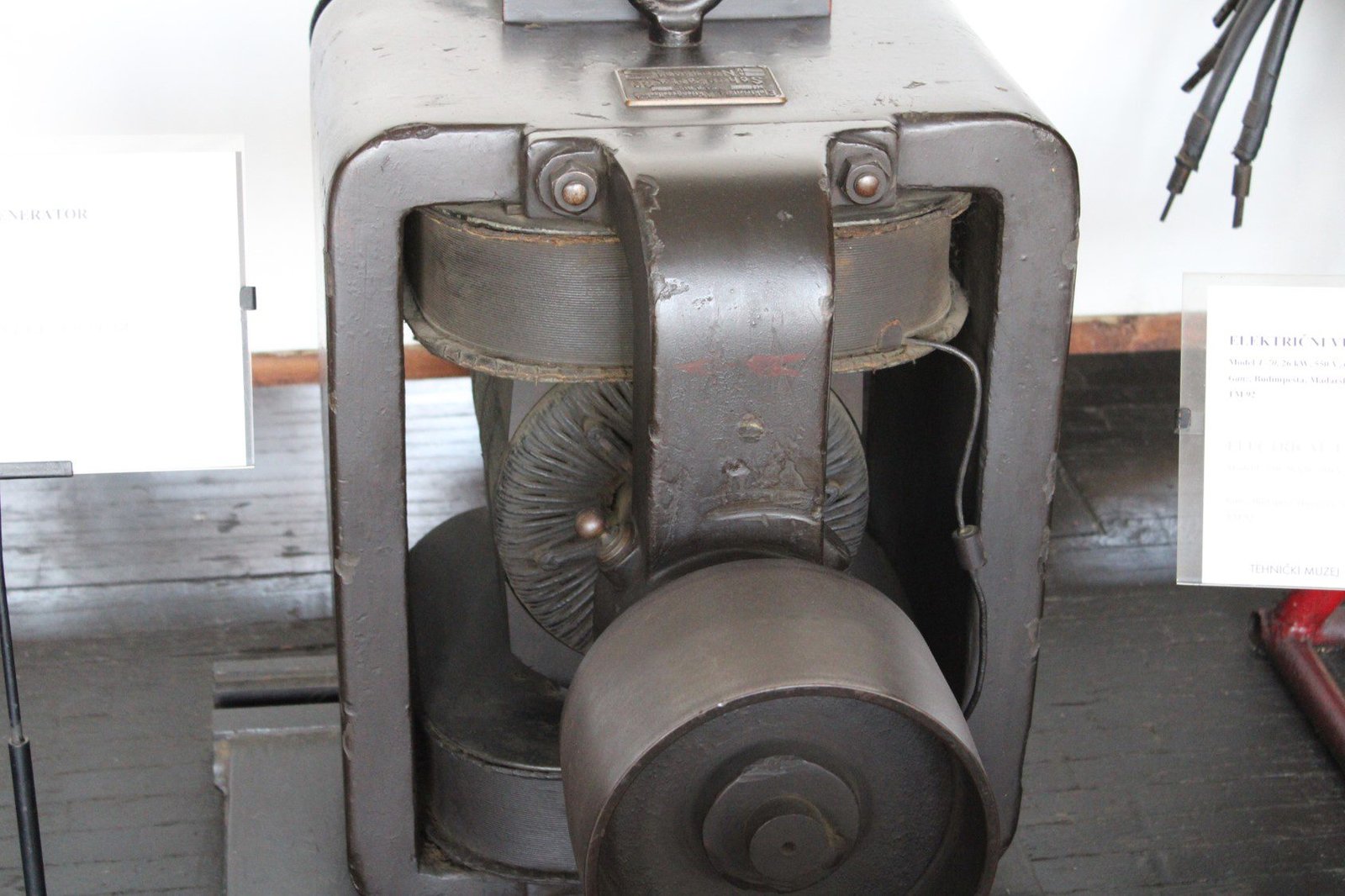
A transformer with air cooling used in hydro power plant OZALJ 1, of Kupa river, Croatia.

Bipolar DC generator AF-8, generated 110 V and 76 A.

Electrical tram motor U-140. 26 kW power, nominal voltage 550 V and 65.5 A of current.

6 kV high voltage switchgear from OZALJ 1. Used in 1908.

OZALJ 1’s control panel from 1908.

Nuclear energy
In this hall, there is a panel dedicated to nuclear energy. This is a model of PWR Westinghouse nuclear power plant.

Protection equipment against radiation. 1 is a dosimeter, an instrument which measures radiation exposure, 2 is the mask to purify air. This suit (3) is made of PVC, has a zip fastener which goes from base of stomach to top of head cover. 4 is a thermo luminescent dosimeter which detects gamma radiation and neutrons. The boots (5) are made of thin plastic and dressed over the shoes. Are conditioned and disposed after use.

Low radiation waste, like plastic boots, are stored in this type of barrel.

To know more about nuclear power plants and uranium, click on buttons below.
Main hall of Technical Museum Nikola Tesla

In main hall there is a submarine and many land transports and aircrafts.
Land vehicles
A small tractor Fiat 50, with 4 cylinder diesel engine and 29 kW, was produced in 1957. It’s maximum speed was 10 km/h and applied in agriculture.


This is a tankette Fiat Ansaldo L35, introduced in 1935.



- Power: 32 kW.
- Maximum speed: 42 km/h.
- Weight: 3500 kg.
- Range: 150 km.
- Armament: 2 8 mm Breda machine guns.
- Crew: 2 (driver and gunner).
Many old bicycles.

The Italian motorcycle Frera from 1912.

- Power: 2.6 kW.
- Magnetic ignition system.
- Weight: 95 kg.
A motorcycle with pedals are called moped. This model is Steyr-Daimler-Puch from Austrian A.G. Graz from 1938.

- Power: 1 kW.
- Carrying capacity: 125 kg.
- Weight: 39 kg.
A motorcycle SB 200 made by German DKW.

- Power: 5 kW at 4000 rpm.
- Maximum speed: 90 km/h.
- Consumption: 3 l/100 km.
The 50 SL made by Tvornica Motora Zagreb (TMZ) in 1959.

- Engine: two-stroke Otto, type 50 N2.
- Gearbox: 2 speeds.
- Fuel consumption: 1.2 l/100 km.
- Max. speed: 50 km/h.
- Weight: 51 kg.
- Tank capacity: 6.2 liters.
This three seats motorcycle was made by Franjo Kahle, in Zagreb, in the 1950s.
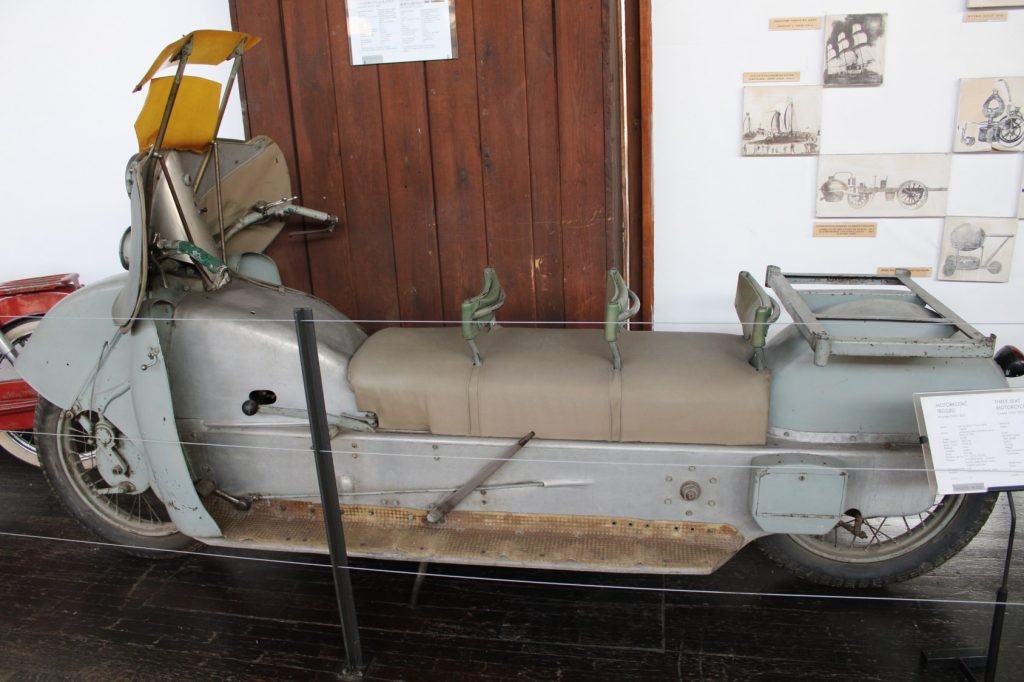
- Power: 8 kW.
- Max. speed: 70 km/h.
- Weight: 250 kg.
- Fuel consumption: 3.5 to 4.5 liters/100 km.
The Prestis NSU Prima V was manufactured in Bosnia and Herzegovina, in 1960.

- Power: 6.8 kW.
- Max. speed: 90 km/h.
- Consumption: 3.4 l/100 km.
- Weight: 128 kg.
The Tomos Colibri T12 is a 1963 Slovenian motorcycle.
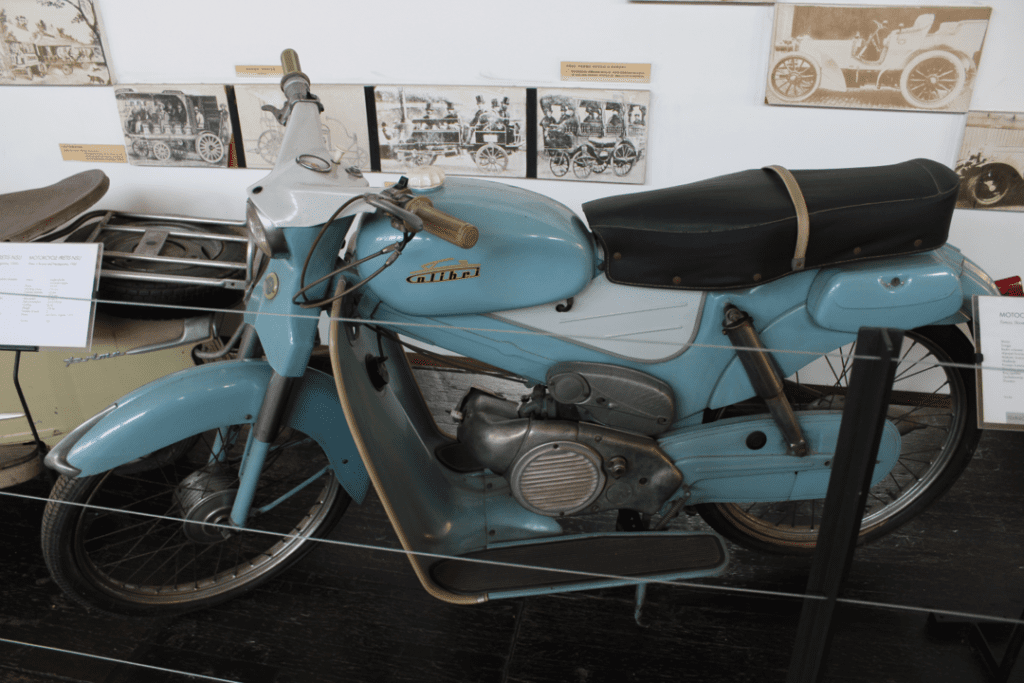
- Power: 1.8 kW.
- Max. speed: 60 km/h.
- Consumption: 2.7 liters/100 km.
A motorized sled, invented by Marko Knez in 1931, whose engine is from a German motorcycle. The steering wheel controls front pair of skis and it’s maximum speed were 30 km/h.

Public transport
A replica of horse-drawn tram from 1891, whose maximum speed were 7.5 km/h.


Steam locomotive Gabor from German Krauss & Company from 1890. Was part of Slavonia-Podravina railway.

- Weight without load: 10 tons.
- Max. speed: 30 km/h.
- Power: 37 kW.
- Max. force: 13,720 N.
1912 tram number 7 from Dubrovnik city, moved by two electric motors. Electrical part was made in Czech Republic and body carriage in Austria.

Aircrafts
This helicopter is Augusta Bell 47J-2A from 1964.
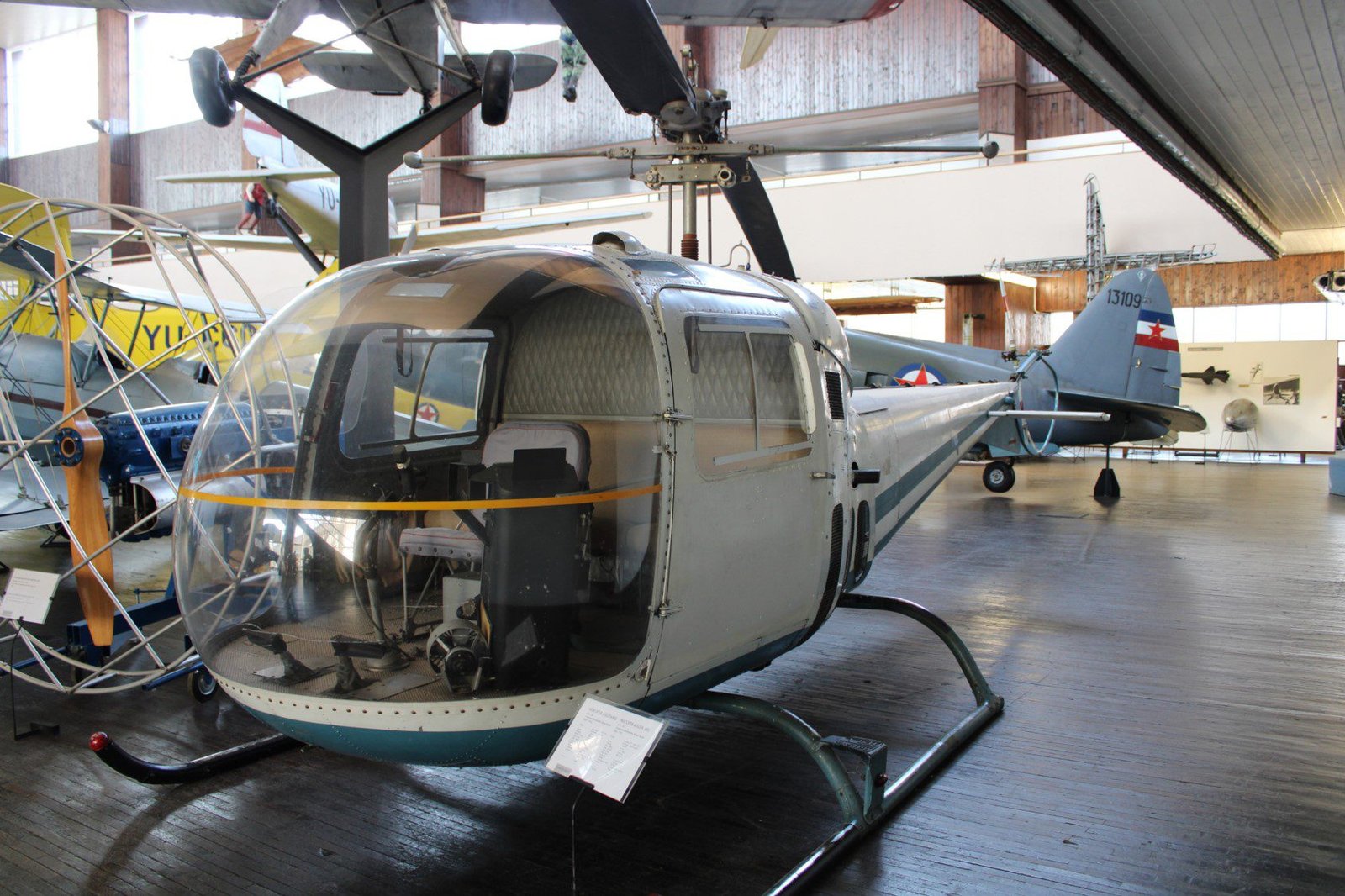
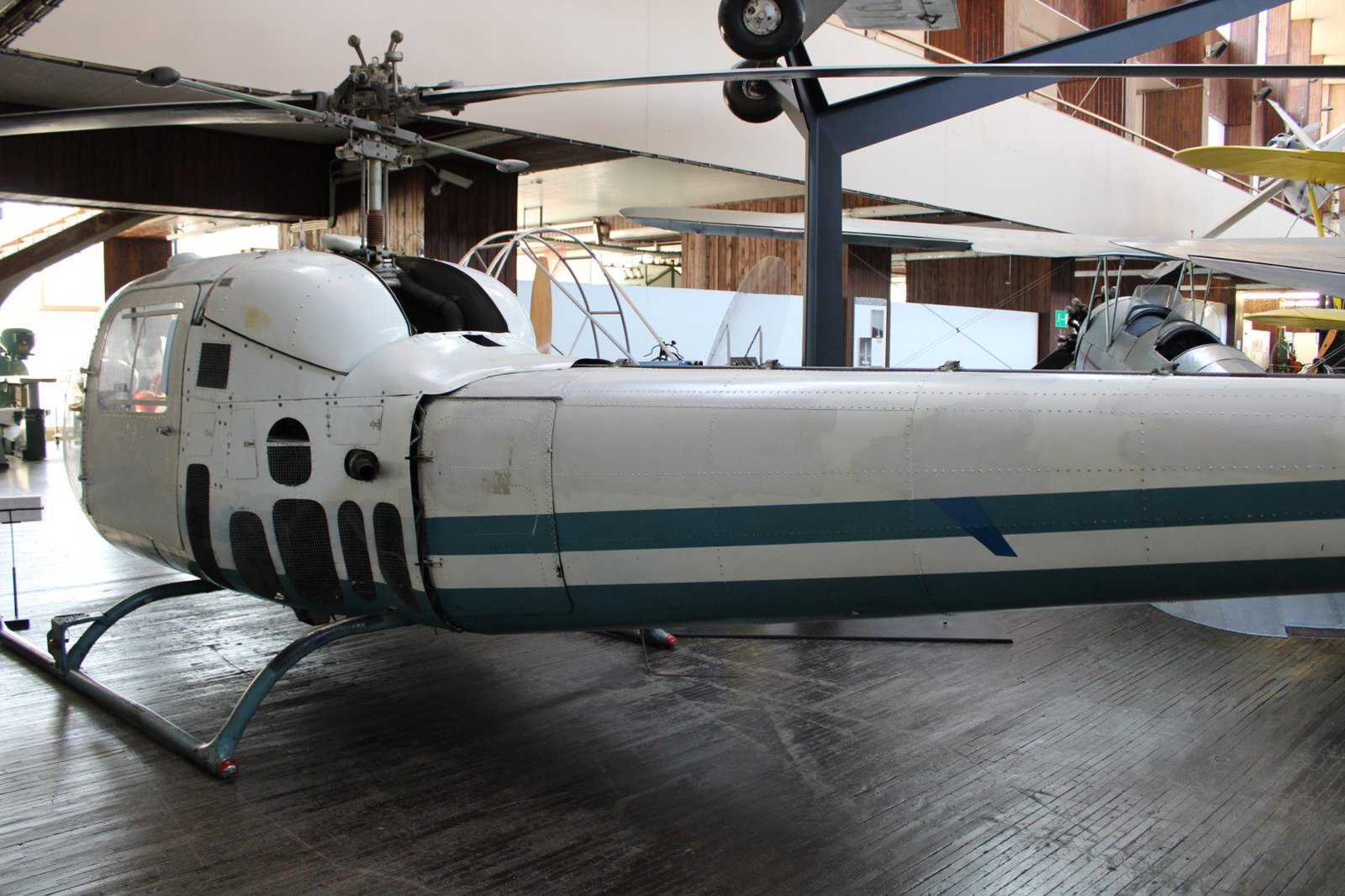


- Engine: Lycoming VO-540 B1B3 with 6 cylinders, cooled by oil.
- Power: 164 kW.
- Max. speed: 169 km/h.
- Max. altitude: 3350 m.
- Range: 400 km.
- Max. time in air: 3 hours and 20 minutes.
- Weight: 1340 kg.
- Capacity: 500 kg.
Training airplane DAR.9 was partially built and assembled under license in Bulgaria during WW2. Was design of German company Focke Wulf Stieglitz.

- Engine: Siemens Schuckert with 7 cylinders cooled by air with 2200 rpm.
- Power: 103 kW.
- Max. speed: 170 km/h.
German biplane Bücker BU-131 Jungmann from 1930s was used in races, training and acrobatic flights. Was built under license in Switzerland, Spain, Japan and Czechoslovakia.



- Engine: Hirth HM 60 r with 4 cylinders and cooled by air.
- Power: 59 kW.
- Max. speed: 170 km/h.
- Max. altitude: 3500 m.
- Flight radius: 680 km.
The floatplane Zmaj Fizir FNH-YU-CGO trained Yugoslavian pilots before WW2 until the 1950s. Designed by Rudolf Fizir. However, some versions didn’t have floaters.
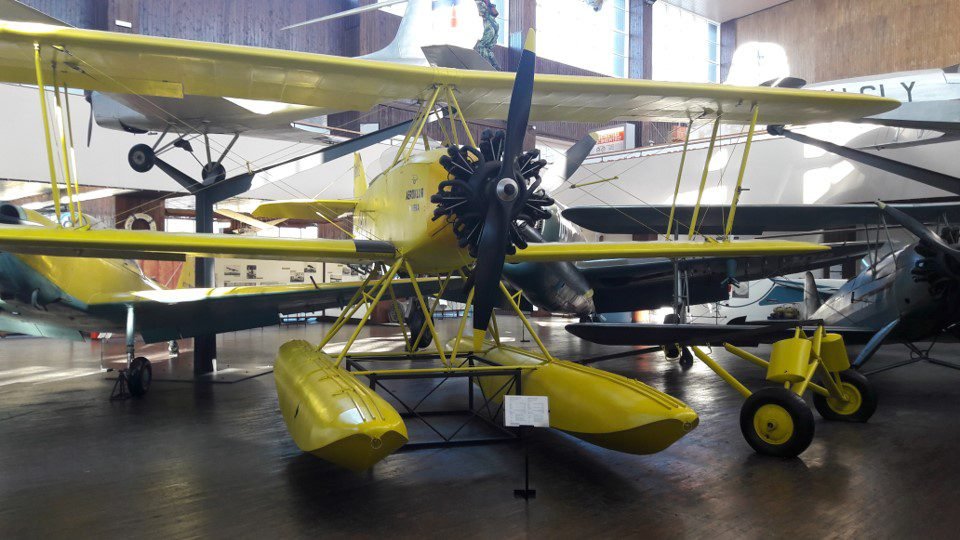


- Weight: 980 kg with full tank and 2 crew members.
- Minimum and maximum speeds: 78 km/h and 160 km/h.
- Engine: Siemens Sh 14 A-4 with 7 cylinders.
- Power: 118 kW (160 HP).
This is the ultra-light Albatroz, made of composites, designed and built in Zagreb by Ljubomir Hranjec, in 1992 and 1993.


- Engine: 50 HP ROTAX 503 with 2 cylinders and cooled by air.
- Weight without load: 147 kg.
- Max. speed: 320 km/h.
- Fuel capacity: 28 liters/2 hours flight.
- Consumption: 3.5 liters/100 km.
The series is not over yet, I will show the submarine, other areas and Nikola Tesla’s laboratory.



