This post’s subject is an introduction to Fly-by-Wire systems on modern airplanes. It’s shown how it works and the advantages in relation to old systems.
Before Fly-by-Wire
In the past, pilot controlled airplane’s actuators (rudder, flaps, ailerons, elevators, spoilers and brake) through pulleys, cranks, steel cables and hydraulic pipes.
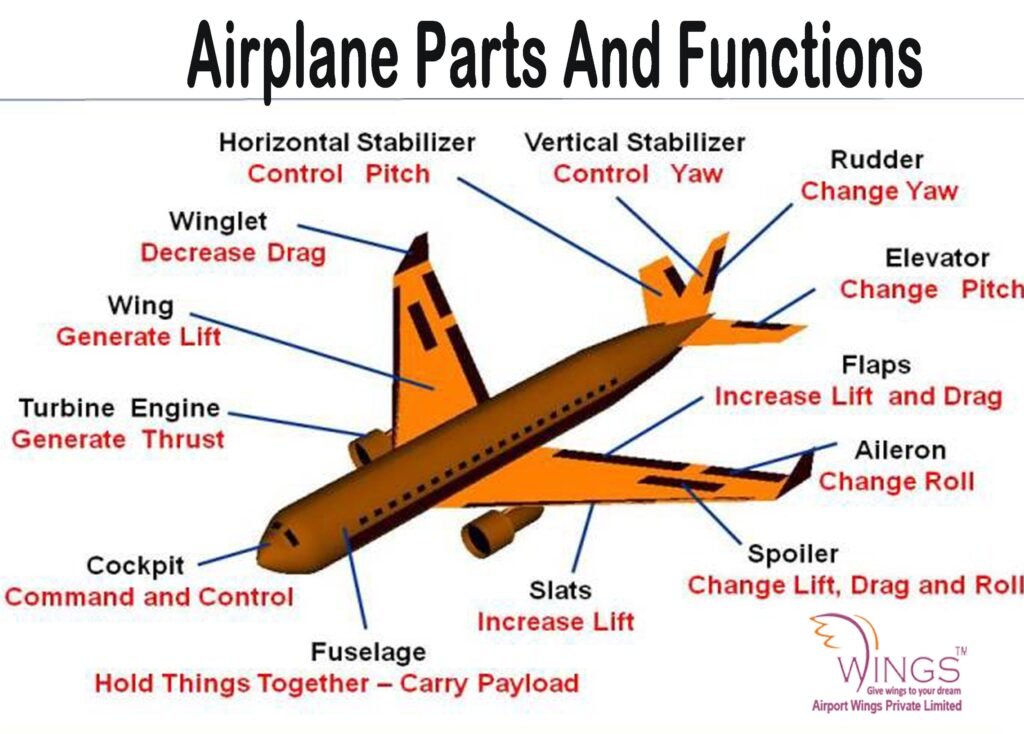
These mechanical systems added too much weight to the plane, in addition to maintenance be longer and more complex.


How it works?
The pilot moves and turns on cockpit’s controls (sidestick, pedals, etc.), they have sensors that convert motions in electric signals, which are transmitted by wires, until arrive to a flight control computer or primary flight computer to make calculations and process input signals. This computer sends signals for actuators to execute movements according to pilot’s commands. Sensors and actuators send feedback signals to computer. It’s a closed-loop system.
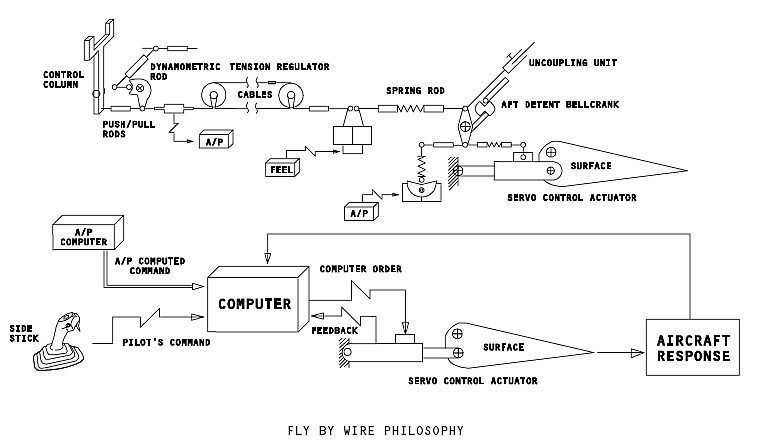
Computers can fail due to electromagnetic interferences or pulses. To increase security, it’s used more than one flight control computer. A computer makes calculations and compare results with others. Defective computers, that obtain different results from others, are reinitialized or shut down.

Each one has 3 lanes, which are central processing units (CPU), they are from different manufacturers, but run the same software. A lane makes data processing, other is on stand-by and another monitor both.
Advantages of Fly-by-Wire
- Substitution of mechanical systems by electronics reduce airplane’s weight. Therefore, saves fuel.
- In case of commercial airplanes, the implementation of Fly-by-Wire allows more space for passengers and luggage.
- Actuators control is more precise.
- More stability and security on flight.
- Less work load for the pilot.
Other technologies
Also exist the Fly-by-Light system, which replaces wires for optic fibers, to reduce interference and increase transmission speed. At the moment, is being developed Fly-by-Wireless, which uses radiofrequency transmitters and receivers, to make communication between computers and components.




