This post subject is LTE, which is the abbreviature of Long Term Evolution. It’s the current technology of mobile telephone.
What is it?
It’s a wireless standard of current fourth generation (4G), used in phones and tablets worldwide. Was developed by 3GPP to improve the 3G mobile communication, with more bitrate and lower latency. Another objective is to unify the communication standards derivated from GSM, CDMA and TDMA.

3GPP is the abbreviation of 3rd Generation Partnership Project, it’s a collaborative project between regulatory bodies to define global standards for wireless communication systems. 3GPP also determined standards for 5G.
The LTE standard is based on IP (Internet Protocol), uses SAE architecture and many antennas in MIMO configuration to meet the requirements for higher speed and less interference. In this technology, data are modulated by the OFDM technique.
SAE (System Archtecture Evolution)
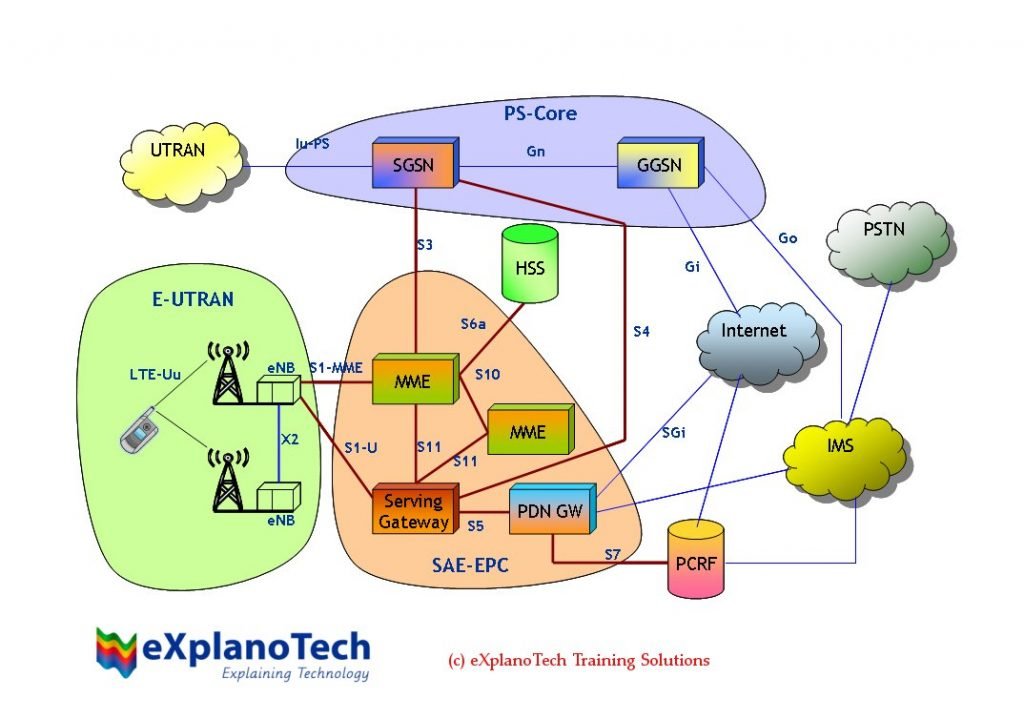
The architecture for LTE is much simpler than the one for 3G. SAE is divided into 2 parts: E-ULTRAN and EPC.
E-ULTRAN
It’s composed of base stations called eNodeB (eNB), they receive and transmit cellphone signals. The latter accesses the network with LTE-Uu interface. An eNodeB communicates with another through x2 interface, which is for control and data transmission. The base stations talk with EPC through S1 interface.
EPC (Evolved Packed Core)
The EPC unifies voice and data in packets for an IP architecture. The components are:
- HSS: Base data where there are user’s information and offers support functions in mobility and configuration.
- Serving Gateway: Transports IP traffic data.
- PDN GW: Packet routers between the Internet and EPC.
- MME: Responsible for security, EPC control, and selection of gateway and SGSN.
PS-Core is part of a network from previous generations.
LTE versions
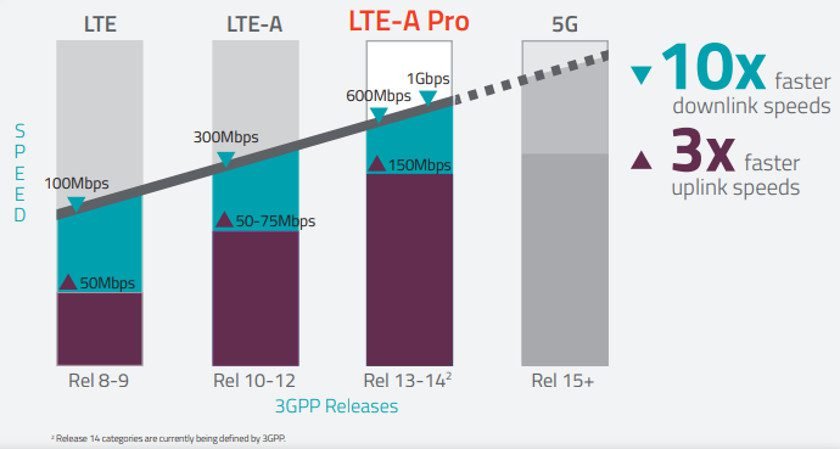
Exist many versions, which are called releases. The first versions were Releases 8 and 9, introduced in 2014, were of third generation because didn’t have the necessary specifications to be 4G. Some sources put it as 3.5G or 3.9G.
LTE-Advanced or LTE-A
LTE-Advanced is 3GPP’s Release 10, meet the requirement to be considered 4G. Has maximum data transmission peak of 3 Gbps in download and 1.5 Gbps in upload and can be modulated in 64 QAM. This standard uses the carrier aggregation technique, providing more operational frequencies for the user.
LTE-Advanced Pro
Created by 3GPP as a transition from 4G to 5G, announced as Release 13. In addition to being faster allows modulation in 256 QAM. The LTE-A Pro will have 4×4 MIMO antennas. While carrier aggregation can provide up to 7 carrier frequencies. The terms and techniques not explained here will be for other posts.